MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT
Advanced driving support technology
that keeps kind eyes on driver
Mazda believes that being able to drive on your own is one of the ways to get more out of life.
With an assumption that a vehicle is driven by human being, Mazda provides advanced driving support technology to keep kind eyes on the driver.
The technology helps the driver to enjoy driving, freedom of travel, and contributes to protecting customer’s lifestyle and the purpose of life.
Mazda delivers the following values to achieve its advanced driving support technology vision.
More safety and peace of mind for all
Technology always keeps kind eyes on the driver, and provides assistance depending on the condition that the driver is in.
When the driver is no longer able to drive, the technology takes over the vehicle control, stops the vehicle safely to prevent grave accidents and reduce damage.
Safer and more flexible driving and travel in different traffic environments
Advanced driving support technology is leveraged to provide enhanced safety and peace of mind in different traffic
environments, including ordinary roads and highways.
Helping different kinds of people gain confidence in driving
and enjoy enriched, liberated driving and travel experience
Mazda helps people, regardless of age and gender, to drive with a purpose, and embrace a more active attitude to life through empowered driving experience.
CONTENTS
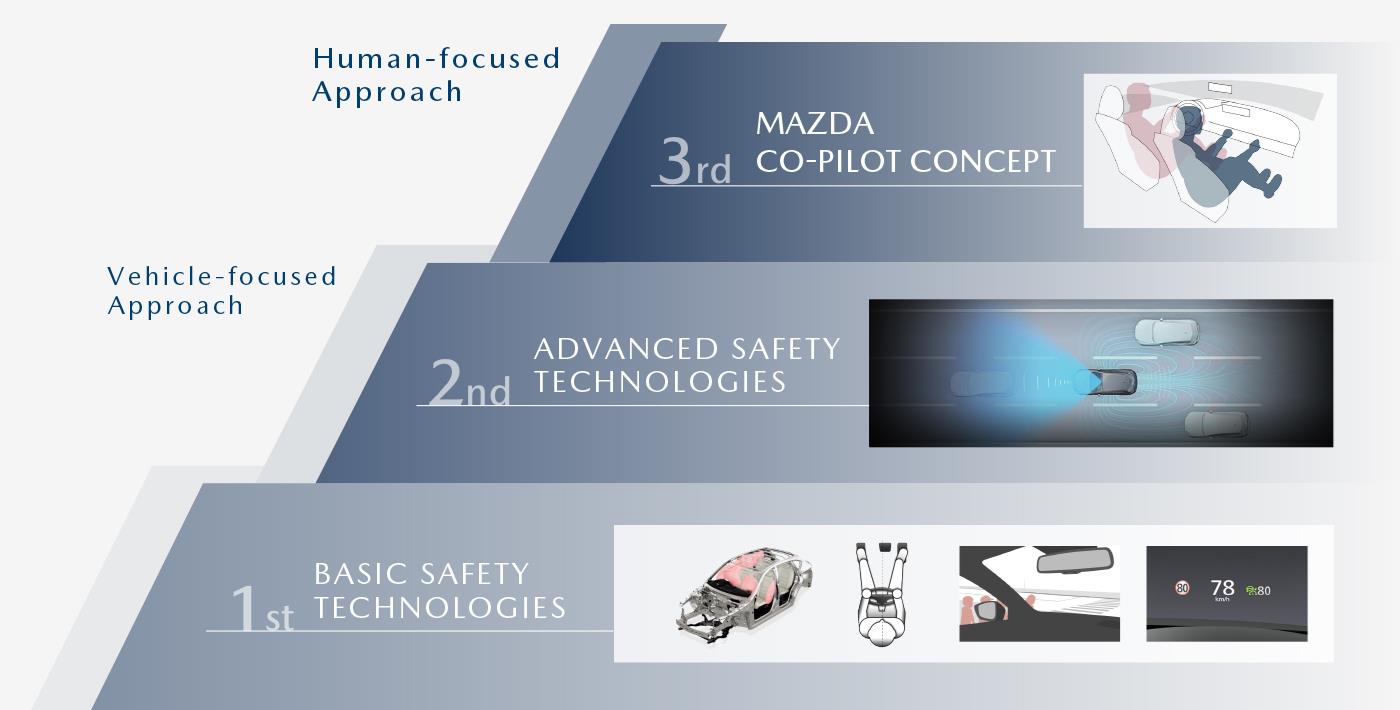
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT
Safety technology for danger prevention and damage reduction
Technology development
for the future


Realizing an automotive society with
enhanced safety and peace of mind
- MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT -
At Mazda, research and development on safety technology is driven by MAZDA PROACTIVE SAFETY – a safety performance concept based on understanding, trusting and respecting the driver, aimed at realizing an accident-free, safe automotive society by letting all the people enjoy the freedom of travel in every region, and by creating a system for people to lead enriched lifestyles.
Yet, there are many challenges that must be overcome to realize the safe automotive society.
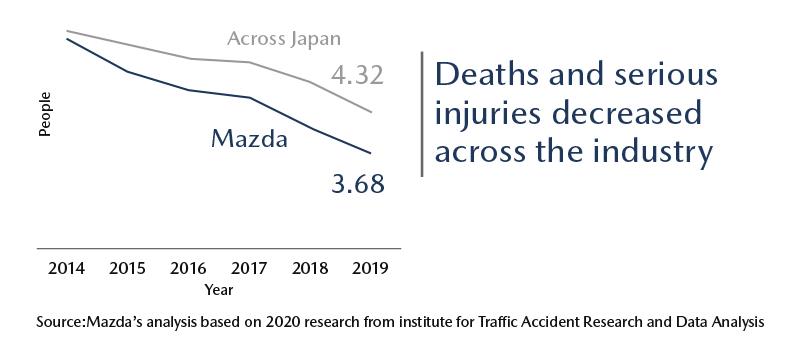
For example, number of fatalities and serious on-road accidents in Japan has been declining year over year,
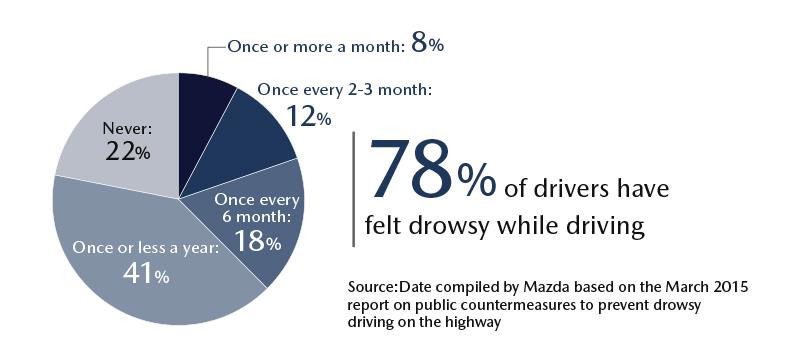
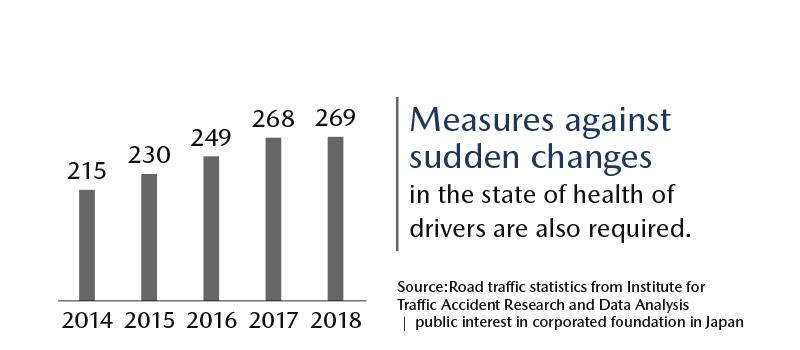
but accidents caused by drivers affected by drowsiness and a sudden change in physical conditions are on the rise.
Today, grave accidents caused by illness and a sudden deterioration of elderly driver’s physical conditions in particular
have become a critical social issue in developed countries.
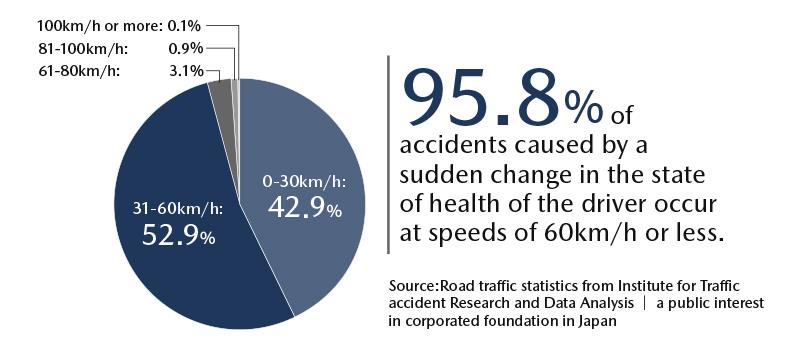
Research on vehicle accidents
(all data shown below are Japanese statistical data)


MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT always keeps eyes on the driver’s condition,
from driving on an ordinary road to cruising on a highway, to help reduce on-road accidents and damage.
In addition to the driver and passengers, Mazda believes that its CO-PILOT CONCEPT can also provide peace-of-mind of the driver’s family,
friends and acquaintances.
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT
An advanced driving support technology concept that aims to reduce potential risks by monitoring driver’s physical conditions.
Advanced safety technology
In addition to active safety technology that supports safe driving by using i-ACTIVSENSE, Mazda’s advanced safety technology that provides recognition support, Pre-crash Safety Technology was developed to avoid collision and reduce damage in a situation where an accident cannot be avoided.
Basic safety technology
Mazda’s basic safety technology covers driving position, pedal layout, driver’s vision and driving visibility, human-machine interface and so on.
MAZDA PROACTIVE SAFETY: Mazda’s safety philosophy for detecting and preventing danger
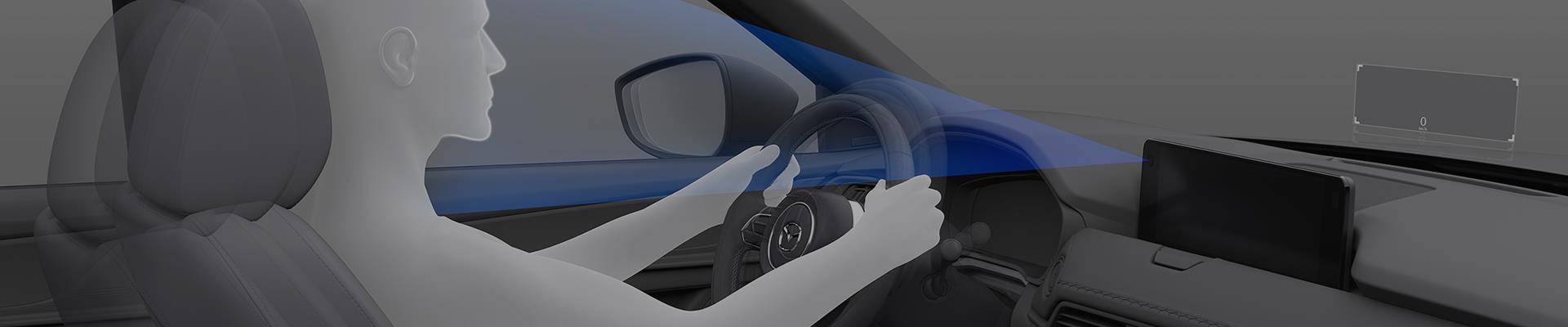
The MAZDA CX-60 is the first model equipped with Driver Emergency Assist (DEA) and Driver Monitoring (DM), both developed based on Mazda’s safety philosophy and intended to reduce potential risks by monitoring driver’s physical conditions.


Safety technology for danger prevention and
damage reduction


Working in connection with Driver Monitoring (DM), DEA keeps eyes on the driver during the entire driving journey on highways, car-limited highways and ordinary roads. When the driver falls suddenly ill and is deemed incapable of driving by the system, DEA takes over the control of the vehicle. The vehicle is decelerated and stopped to prevent potential accidents and minimize damage.
Once the vehicle is stopped safely, DEA unlocks the door and makes an emergency call by automatically connecting to HELPNET
to ensure prompt driver relief and rescue.
* Japanese specification
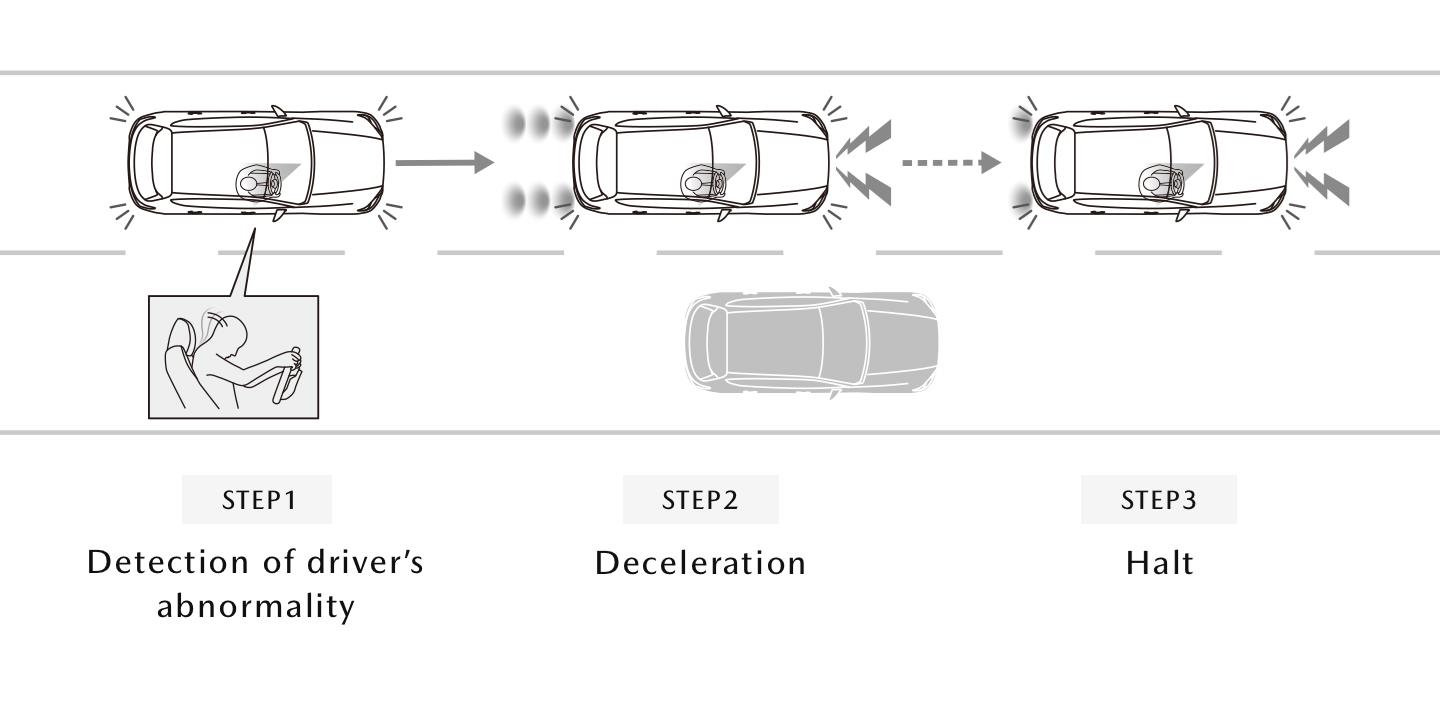
STEP1
DEA monitors the driver’s conditions. Once abnormality is detected, the system starts to flash hazard warning lights to let passengers know that the vehicle will come into an emergency stop.
STEP2
If the driver is deemed no longer capable of driving, the system starts flashing brake lights and beeping the horn in addition to flashing hazard lights to let other drivers and pedestrians on the road know of the emergency. The vehicle is decelerated and stopped.
STEP3
The system automatically makes an emergency call to an external emergency report system as necessary.
* Connected Service contract is required for the emergency call function.


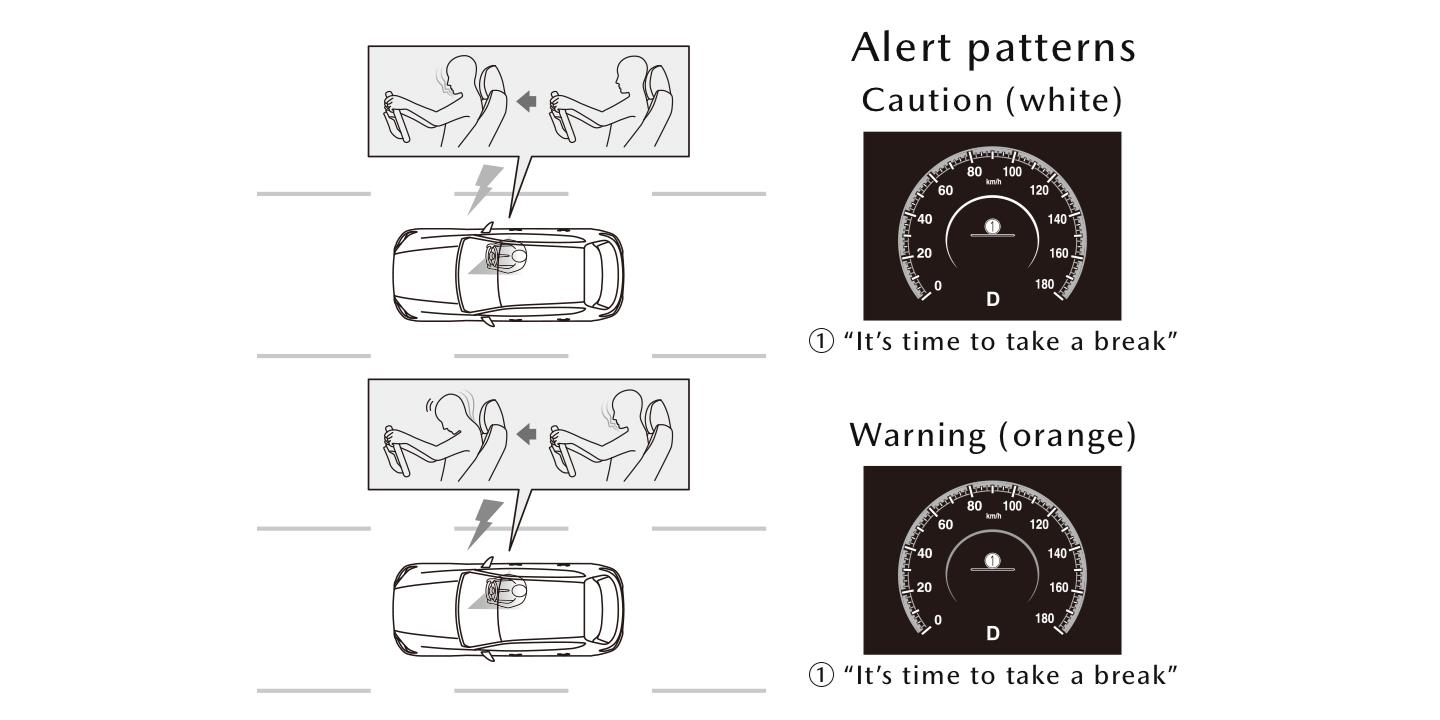
True to its name, Driver Monitoring (DM) keeps attentive eyes on the driver. When the system detects inattentive driving behavior, an alert is sent to remind the driver of driving risks. If the driver’s fatigue or drowsiness is detected, the system prompts the driver to take a break.
The system uses driver monitoring cameras to detect any changes in the driver’s characteristic facial features and makes a presumption on potential fatigue and drowsiness. The system displays messages on Multi-information Display, and makes an alert noise to encourage the driver to take a break.
Once the driver’s inability to drive is detected, such as falling asleep or a rapid deterioration of physical conditions, the system connects with DEA to support prevention of potential accidents and minimize damage.
* Japanese specification
- DEA: Driver Emergency Assist
- DEA is a system based on an assumption that a driver is responsible for safe driving. It is intended to reduce damage caused by accidents and physical burden on driving.
The system is started under certain conditions, and functions are restrictive in nature. Drivers are strongly encouraged to drive safely without overreliance on the system. - This system is not intended to aid sleep driving and driving under deteriorated physical conditions.
- Lane keeping and pulling a vehicle off to the side of the road are subject to certain operating conditions.
- Vehicle deceleration and stop while pulling off to the side of the road requires a use of an SD card for car navigation system.
- Emergency call by automated connection requires a connected service contract.
- The system may not operate as intended when the driver frequently changes the direction of his/her face, parts of the driver’s eyes and face are concealed, or a significant change in lighting conditions is detected.
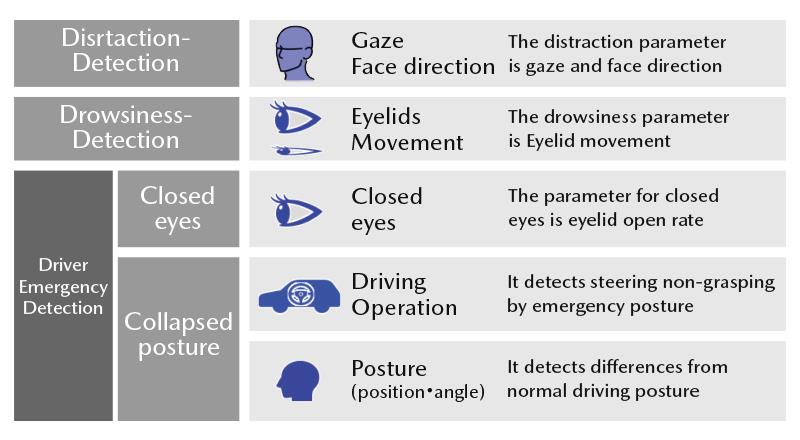
- Emergency detection (inattentive driving, drowsiness, sleep driving) decision parameters
-


Technology development
for the future
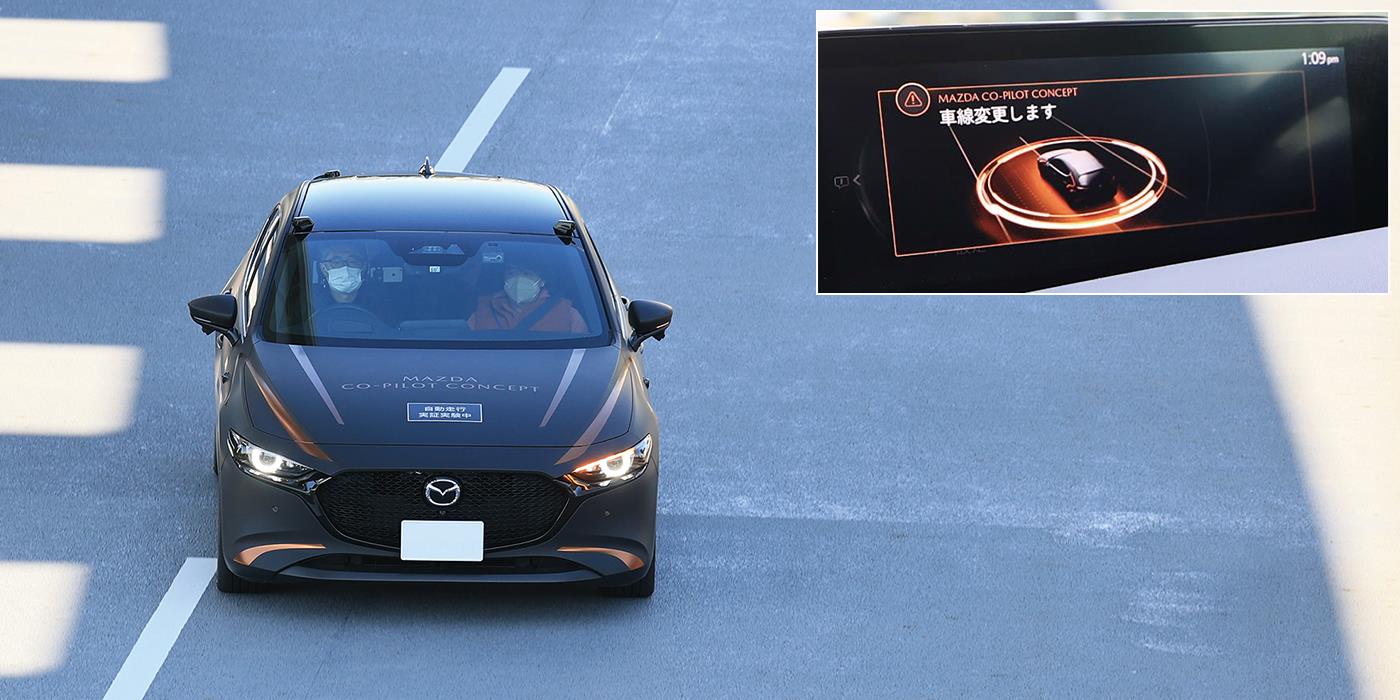

As a part of its next-generation advanced driving support technology development,
Mazda is working on technologies and conducting substantiative experiments under different driving environments.
- Photo above was taken at MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT Technology Demonstration in 2021 at Odaiba, Tokyo.
- A technology prototype vehicle shown in the photo.
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT Roadmap
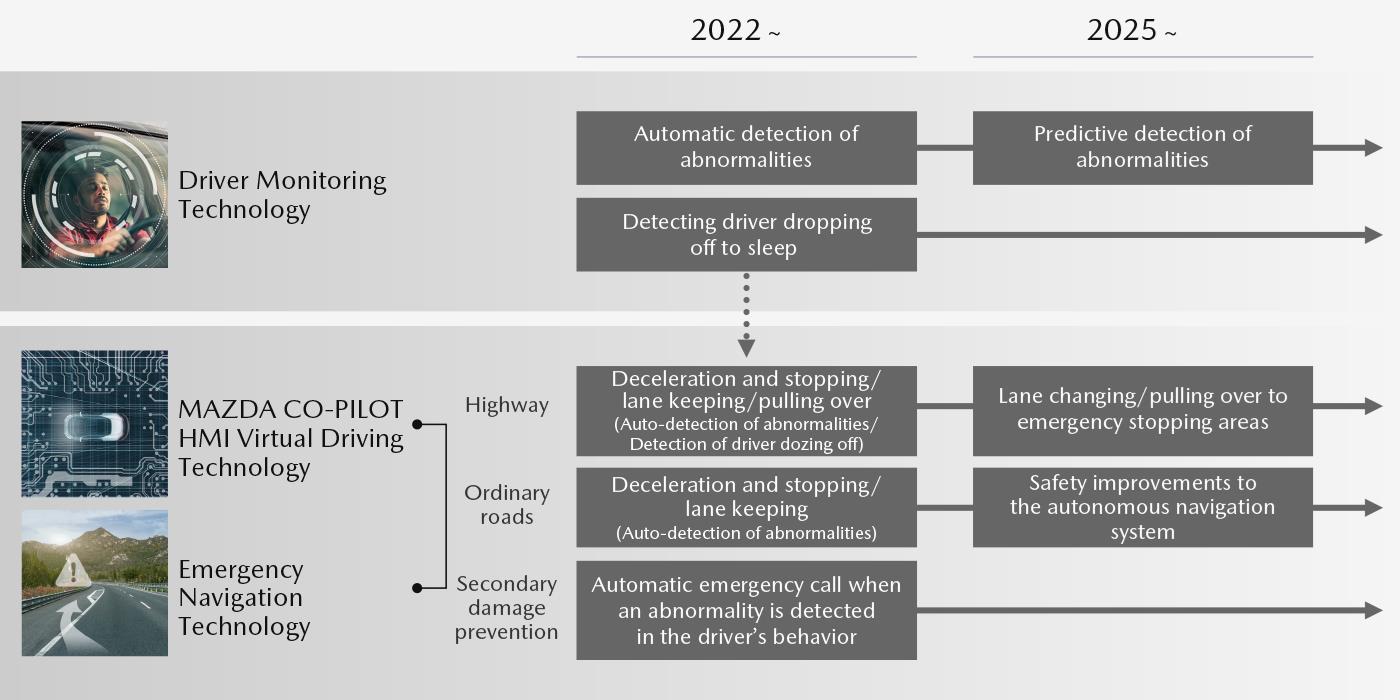
In 2025 and beyond, Mazda strives to evolve its advanced driving support technology to a new height:
detecting early signs of driver’s deteriorating physical conditions, taking control over the vehicle for a lane change and pulling the vehicle over to the side of the highway, and taking the vehicle to stop at a safe place on ordinary roads.
Driver’s abnormal signs detection technology
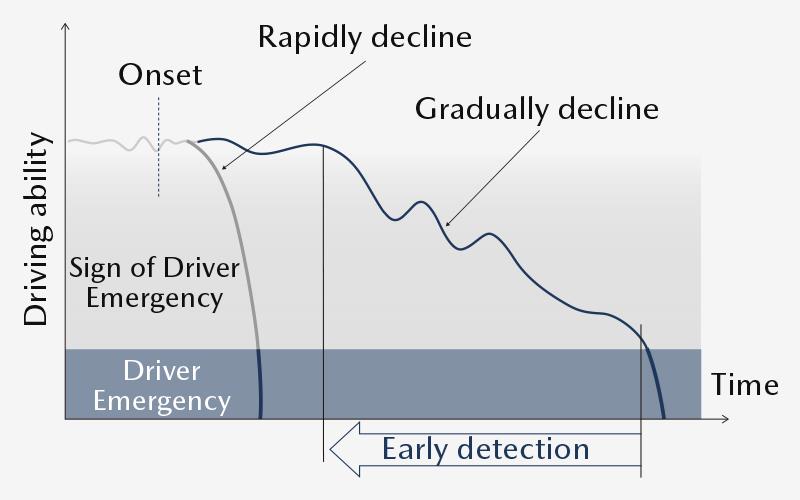
By detecting early signs of driver’s abnormality and taking over the control of the vehicle more in advance, before the driver becomes incapable of driving, Mazda aims to further reduce risks of causing an on-road accident and to better secure safety of the driver and the vehicle, as well as other cars and pedestrians on the road.
- Gaze anomaly detection by saliency map (gaze behavior)
-
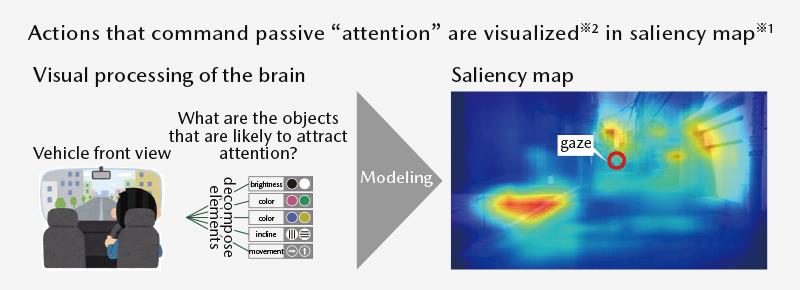
The human gaze behavior is categorized into “conscious behavior” and “unconscious behavior.”
Conscious behavior involves looking at potential danger, and intentionally checking mirrors and gauges. Conversely, unconscious behavior involves passively called to attention, such as looking at something that is visually salient. Under normal circumstances, the driver balances these two behaviors when moving his/her gaze. But when the driver begins to undergo cerebral dysfunction, the gaze is biased toward areas and subjects that attract passive attention.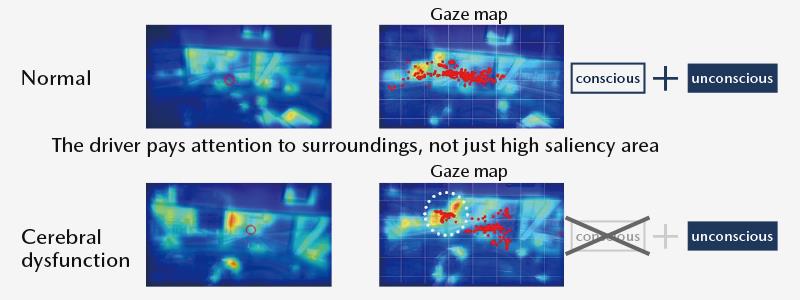
Using neuroscientific knowledge and insights, Mazda has been conducting research and study for detecting the state of cerebral dysfunction. An algorithm for real-time identification of subjects that are most likely to attract the driver’s gaze during driving was developed, to assist development of technology that can detect characteristic changes under regular circumstances and at cerebral dysfunction, and spot early signs of the driver’s abnormalities.
- Properties that induce attention
- Outcome of joint study with COI, Hiroshima University
RELATED VIDEOS
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT presentation video
(duration: 13 minutes 54 seconds)
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT demonstration driving scene(driving on ordinary road) video ~ Technology planned for introduction in 2025 and beyond ~
(duration: 1 minute 41 seconds)
MAZDA CO-PILOT CONCEPT demonstration driving scene(driving on freeway) video ~ Technology planned for introduction in 2025 and beyond ~
(duration: 3 minute)